The importance of Air Ducts and Registers
What Are Air Ducts and Registers?
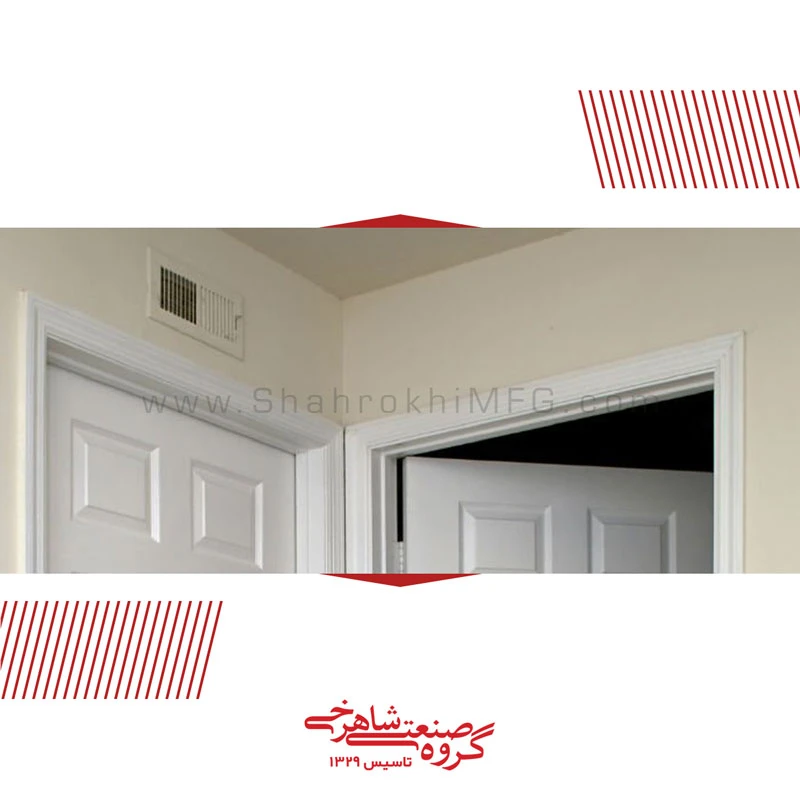

Air ducts are the intricate system of tubes and related parts that distributes the airflow of your air conditioner (and HVAC system at large) throughout your home or commercial building.
Registers at the end of each air duct direct the airflow within a room or space. Supply air registers are not returns; they do not bring air back into an HVAC system. A return will have a permanent, unmovable grille. In addition, supply air registers and returns are also called “vents”.
Where Are Air Ducts & Registers Located?
Air ducts are located behind walls and floors and are visible in crawlspaces, attics, and basements or cellars. Some split-system air conditioners do not use conventional ducting, though ductless air conditioning may not be right for all homes or businesses.
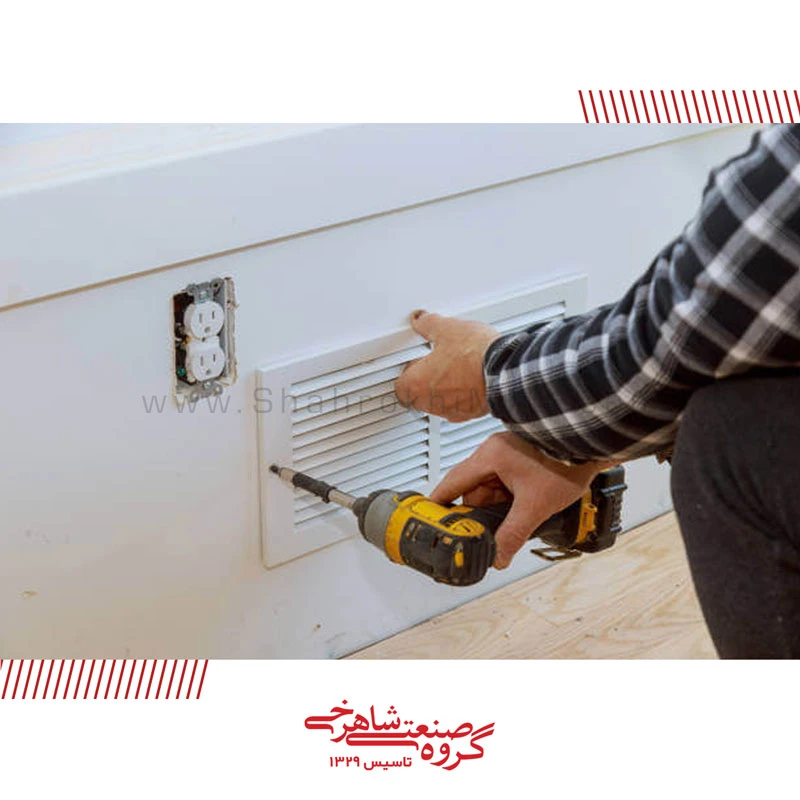
Registers are installed on metal cans in the opening of a wall. For example, either up high toward the ceiling or near the base of a wall. Also registers are found in floors in older homes .

How Do They Each Work?
Apart from the air ducts themselves, ducting includes other crucial components:
- Vibration isolators, which minimize an operating HVAC system’s vibration
- Metal cans allow the flow of air to move from the ducts to the registers
- Dampers, which adjust the volume of air
- Vanes, which smooth out air flow around turns
in order to have a balanced, comfortable home, careful sizing and placement of return and supply air ducts and registers is important.
Registers have bars that you can control with an adjustable damper (a lever, knob, or another movable part on one side of the register) to reduce or direct airflow.
What Makes Them Important?
Ducting acts as the arteries and veins of your air conditioning system. They deliver the right amount of cool air to each room in your home or commercial space.
Registers help control the comfort level of a space by providing a way to direct airflow at the point it enters a room.






Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!